前言
操作系统系列博客的所有实验源自于课程"操作系统原理与实践检验",代码是参考老师给的"软件工程专业操作系统实验指导书"文档后的改进版本。操作系统是计算机系统的核心,因此了解操作系统的设计和实现思路是必不可少的。了解操作系统的基本要求是:理解进程的概念,理解死锁,掌握银行家算法;掌握页式储存管理的实现原理以及页面置换法
实验目的
- 掌握进程状态转换过程
- 掌握时间片轮转的进程调度算法
- 掌握带优先级的进程调度算法
实验内容
- 自定义PCB的数据结构
- 使用带优先级的时间片轮转调度算法进行进程调度,每运行一个时间片,进程优先级减半
- 需要完成的命令集:
create:随机创建进程,进程的优先级与所需要的时间片随机决定round:执行一次时间片轮转操作,其方法为运行高优先级队列的第一个,再降低其优先级,插入到相应的队列中ps:查看当前进程状态sleep:将一个就绪的进程挂起awake:唤醒一个被挂起的进程kill:杀死一个进程help:系统帮助quit:退出系统
实验过程
本次实验结合了进程的状态转换、优先级调度、时间片轮转调度,这三个方面的内容。根据进程状态转换图,设置sleep命令,将一个进程挂起;awake命令唤醒一个被挂起的进程(从阻塞状态到就绪状态)
优先级
优先级体现了进程的重要程度或紧迫程度,在大多数现代操作系统中,都采用了优先级调度策略。优先级从小到大(如0-127)逐渐降低,0的优先级最高,127的优先级最低。在本次实验中,进程的优先级分为3个等级(0-2),数值越大,优先级越高
基于时间片调度
将所有的就绪进程按照先来先服务的原则,排成一个队列,每次调度时,将CPU分配给队首进程,并令其执行一个时间片。当时间片用完时,由一个计时器发出时钟中断请求,调度程序把此进程终止,然后把该进程放到队尾
在本次实验中,时间片以大约1000ms为单位(实际上要小得多),使用双重for循环实现。在调度过程中,需要通过时间函数检测进程的执行时间,当该进程执行时间>=时间片大小时进行调度
高优先级调度
优先级高的进程先得到CPU,等该进程执行完毕后,另外的进程才能执行
基于时间片的高优先级调度
在调度算法中,只有处于就绪状态的进程才能被调度,调度算法结合了优先级调度和时间片轮转调度算法,约定:从最高优先级队列取第一个就绪状态的进程进行调度,时间片到后降低其优先级(降低一半),然后插入到底优先级队列的尾部,每次调度后,显示进程的状态
代码汇总
由于实验的代码比较长,这里采用分块的方法来进行代码汇总
定义系统常量,数据结构,初始化函数
需要的系统常量有:系统最大进程数、最高优先级、时间片大小、命令列表
定义的数据结构:进程控制块PCB、priority_array优先级数组+链表,数组用于记录不同的优先级链表中的第一个进程,其余同优先级进程使用链表进行储存、id_list,记录进程的创建状况
init函数:初始化优先级链表,将其置为NULL。初始化命令列表,一共有8条命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| # include <cstdlib>
# include <iostream>
# include <cstring>
# define PROCESS_NUMBER 10
# define MAX_PRIORITY 3
# define QUANTUM 2
struct pcb
{
int id;
int status;
int prio;
int life;
pcb *next;
} *priority_array[MAX_PRIORITY];
static int id_list[PROCESS_NUMBER];
int life = 0;
char command[8][10];
void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_PRIORITY; i++)
{
priority_array[i] = NULL;
}
strcpy(command[0], "quit");
strcpy(command[1], "help");
strcpy(command[2], "ps");
strcpy(command[3], "create");
strcpy(command[4], "kill");
strcpy(command[5], "runtime");
strcpy(command[6], "sleep");
strcpy(command[7], "awake");
}
|
输出当前系统状态信息
ps函数:使用优先级数组+链表的数据结构,可以很容易按照优先级进行遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
void ps()
{
struct pcb *p;
printf("\n=================================================\n");
printf("Total system life: %d\n", life);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_PRIORITY; i++)
{
printf("Priority level: %d\n", i);
p = priority_array[i];
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("id: %d, status: %d, priority: %d, life: %d\n", p->id, p->status, p->prio, p->life);
p = p->next;
}
}
printf("=================================================\n\n");
}
|
创建新进程
create函数:按照顺序分配一个进程ID,随机分配进程优先级和进程生命周期,然后插入到相应的优先级链表中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
void create()
{
int i = 0, prio = 0, plife = 0;
struct pcb *p = NULL, *p_previous = NULL, *s = NULL;
while (id_list[i] != 0 && i <= PROCESS_NUMBER - 1)
i++;
if (PROCESS_NUMBER == i)
{
printf("System max process error!\n");
return;
}
id_list[i] = 1;
prio = rand()%MAX_PRIORITY;
plife = rand()%20 + 1;
life += plife;
s = new pcb;
s->id = i;
s->status = 0;
s->prio = prio;
s->life = plife;
s->next = NULL;
p = priority_array[prio];
if (p == NULL)
priority_array[prio] = s;
else
{
while (p != NULL)
{
p_previous = p;
p = p->next;
}
p_previous->next = s;
}
printf("Successfully create process(id: %d), current system status: \n", i);
ps();
}
|
阻塞/唤醒线程
sleep/awake函数:这两个函数的操作基本一样,都是找到进程后修改进程的状态码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
|
void sleep(int x)
{
int i = 0, find = 0;
struct pcb *p = NULL;
while (!find && i!=MAX_PRIORITY)
{
p = priority_array[i];
if (p == NULL)
{
i++;
continue;
}
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->id == x)
{
find = 1;
break;
}
else
p = p->next;
}
if (!find)
i++;
else
break;
}
if (!find)
{
printf("Sleep: Invaild process number!\n");
return;
}
if (p->status == 2)
printf("The process(id: %d) has been blocked, cannot sleep again!\n", x);
else
p->status = 2;
ps();
}
void awake(int x)
{
int i = 0, find = 0;
struct pcb *p = NULL;
while (!find && i!=MAX_PRIORITY)
{
p = priority_array[i];
if (p == NULL)
{
i++;
continue;
}
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->id == x)
{
find = 1;
break;
}
else
p = p->next;
}
if (!find)
i++;
else
break;
}
if (!find)
{
printf("Awake: Invaild process number!\n");
return;
}
if (p->status != 2)
printf("The process(id: %d) has been awaked, cannot awaked again!\n", x);
else
p->status = 0;
ps();
}
|
杀死进程
kill函数:首先找到进程的位置,将其从优先级链表上摘下来后删除,同时id_list相应位置置为0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
void kill(int x)
{
int i = 0, find = 0;
struct pcb *p = NULL, *p_previous = NULL;
while (!find && i!=MAX_PRIORITY)
{
p = priority_array[i];
if (p == NULL)
{
i++;
continue;
}
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->id == x)
{
find = 1;
break;
}
else
{
p_previous = p;
p = p->next;
}
}
if (!find)
i++;
else
break;
}
if (!find)
{
printf("Kill: Invaild process number!\n");
return;
}
if (p == priority_array[i])
{
priority_array[i] = priority_array[i]->next;
id_list[x] = 0;
life -= p->life;
delete p;
}
else
{
p_previous->next = p->next;
id_list[x] = 0;
life -= p->life;
delete p;
}
ps();
}
|
时间片运行
runtime函数:模拟运行一个周期,然后降低该进程的优先级,如果该进程未运行完成,则将该进程节点移动到新的优先级链表上,如果已经运行完成,则执行kill函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
void runtime()
{
int i = MAX_PRIORITY - 1, prio = 0, t = 0;
struct pcb *pp = NULL, *qq = NULL, *r_previous = NULL, *r = NULL;
do
{
while (i >= 0 && priority_array[i] == NULL)
i--;
if (i < 0)
{
printf("No process in the system, create/awake a process and try again!\n");
return;
}
r_previous = priority_array[i];
r = priority_array[i];
while (r != NULL && r->status != 0)
{
r_previous = r;
r = r->next;
}
i--;
} while (r == NULL);
printf("Process(id: %d) gain the CPU time and will execute %d quantum\n", r->id, QUANTUM);
r->status = 1;
printf("Process %d is running......\n", r->id);
for (int j = 0; j < 600000; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 1000; k++)
{
}
}
printf("Time out, change to ready status, reduce priority\n");
r->status = 0;
r->prio /= 2;
if (r->life - QUANTUM > 0)
{
r->life -= QUANTUM;
life -= QUANTUM;
}
else
{
life -= r->life;
r->life = 0;
}
if (r->life == 0)
{
printf("Process %d completed, now release it!\n", r->id);
kill(r->id);
}
else
{
if (r_previous == r)
priority_array[i+1] = r->next;
else
r_previous->next = r->next;
t = r->prio;
pp = priority_array[t];
while (pp != NULL)
{
qq = pp;
pp = pp->next;
}
if (qq == NULL)
priority_array[t] = r;
else
qq->next = r;
r->next = NULL;
}
ps();
}
|
命令行控制台和系统主入口
命令控制台和系统主入口都很好理解,这里就不多说了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
void terminal()
{
char cmdstr[32];
int cmd = 0, id = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("cmd: ");
scanf("%s", cmdstr);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if (!strcmp(command[i], cmdstr))
{
cmd = i;
break;
}
}
switch (cmd)
{
case 0:
return;
case 1:
printf("\n=================================================\n");
printf("id: 当前进程ID status: 进程状态:0-就绪,1-运行,2-阻塞 prio: 进程优先级 life: 进程生命\n");
printf("随机创建一个新进程: create\n");
printf("杀死一个进程: kill\n");
printf("使一个进程进入阻塞状态: sleep\n");
printf("唤醒一个进程: awake\n");
printf("查看当前进程信息: ps\n");
printf("运行一个时间片周期: runtime\n");
printf("获取帮助: help\n");
printf("退出: quit\n");
printf("=================================================\n\n");
break;
case 2:
ps();
break;
case 3:
create();
break;
case 4:
printf("Which process you want to kill: ");
scanf("%d", &id);
kill(id);
break;
case 5:
runtime();
break;
case 6:
printf("Which process you want to sleep: ");
scanf("%d", &id);
sleep(id);
break;
case 7:
printf("Which process you want to awake: ");
scanf("%d", &id);
awake(id);
break;
default:
printf("Error command!\n");
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
init();
terminal();
return 0;
}
|
实验测试
编译并运行程序,早上编译的时候按多了一下Tab键,导致cpp源文件直接被覆盖重写成了二进制文件,重写代码花了1个小时,有时候Tab键真的能坑死人😂
1
2
| g++ dispatcher.cpp -o dispatcher
./dispatcher
|
使用help命令查看帮助信息
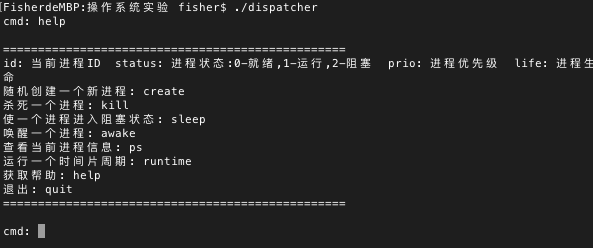
创建多个进程,进程超过系统上限后就无法创建了,然后查看系统进程状态
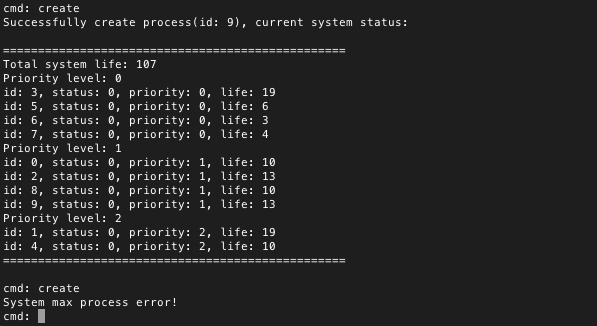
阻塞/唤醒一些进程,使系统进程有不同的状态。尝试重复阻塞/唤醒某些进程,看看系统能否检查出错误操作
图中可以看到,我将3,0,2,1,4号进程阻塞,7号进程是阻塞后又唤醒的进程
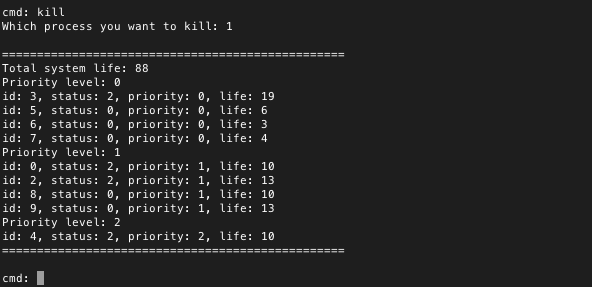
杀死进程,检查进程是否从优先级链表中移除
图里可以看到,我将ID为1的进程杀死之后,系统状态中已不存在ID为1的进程
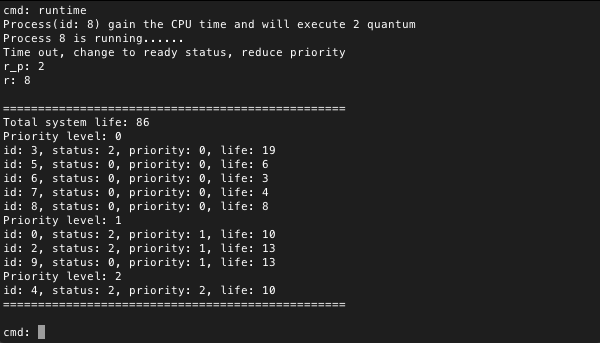
运行一个时间片
可以看到0,2,4号进程因为阻塞状态而不运行,系统选择了8号进程运行,时间片走完之后,8号进程的优先级减半,并且插入到优先级为0的等待队列中
总结
本次实验我们模拟了操作系统中的进程调度,我们使用的调度算法是最高优先级的调度算法,即从等待队列中取出优先级最高的进程运行。该算法的好处是保证了高优先级的进程获得更多的时间片,缺点在于如果不断有新的高优先级进程加入等待队列,低优先级的进程获得时间片的概率很低。该算法的时间复杂度为O(n),只需要运行一次扫描就能选取出优先级最高的进程,空间复杂度也同样为O(n),只需要指针进行标记,不需要额外的空间就能进行进程的调度。在现代操作系统中,系统通常选取多种不同的算法来进行进程的调度,尽量保证每个进程获得CPU时间片的概率是相同的
课后思考
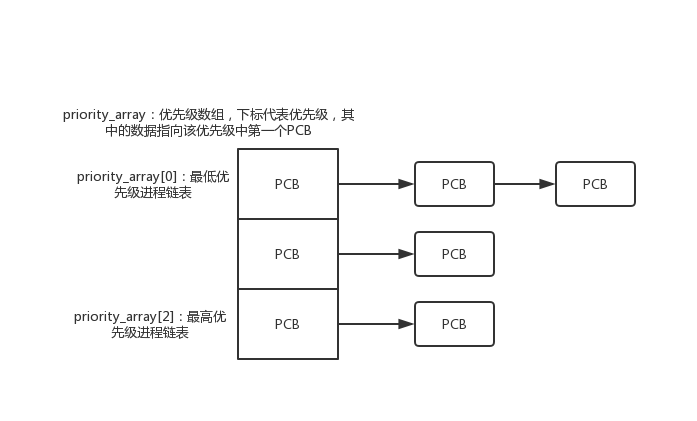
读懂程序,画出算法所用的数据结构简图
该算法的数据结构很简单,一个类型为PCB指针的数组,下标代表优先级,在本次实验的定义中,下标越大优先级越高,数组中的元素是该优先级链表中的第一个PCB。在算法执行过程中,只需要取优先级最高,并且为就绪状态的PCB即可,这需要一个for循环:用于优先级数组遍历,和一个while循环:用于链表的遍历,即可选出对应的PCB
修改runtime函数,使得算法能够模拟运行中的进程被外界中断或因设备请求而不能运行,自动转入阻塞状态并进行调度
答:在执行过程中的两个for循环处加上对该进程的sleep操作和runtime递归调用即可,如果该进程的优先级不需要减半,再加上return终止此次调度即可






